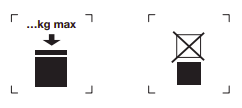ADR (Transport of Dangerous Goods by Road) has been consolidated in its most recent iteration by the arrested due 29 May 2009 (modified) involve a great deal of transfer of hazardous materials by land, also known as the “arrested TMD,” which applies to transportation conducted on national territory.
This specific regulation for the transportation, loading and unloading of dangerous goods fits into a logical accident-prevention strategy, complementing, for example, the requirements of the labor code.
This article’s goal is to present you with the ADR’s general obligations:
Classifying and identifying cargo, encasing, etiquette, and marking cargo, establishing transportation documents, adhering to loading/unloading conditions, signaling and equipping the transport vehicle, training the driver and all other personnel involved, and designating a safety advisor; all while explaining how each of these points contributes to risk prevention.
To assist you in the daily management of hazardous materials handling in the context of your transportation-related activities.
To make it easier to use the ADR, simplify your understanding of its major points.
To help each participant better understand the risks, responsibilities, and challenges that arise in the transportation and logistics chain.
ADR in practice
What is a dangerous product, according to the ADR?
According to the ADR, a product is dangerous if it poses a risk to humans or the environment. It then responds to various ranking criteria.
It could be a substance, an object, a solution, a mixture, a preparation, or a waste.
All dangerous goods for road transport are either specifically mentioned or covered by ADR generic rubrics.
What documents will we need to provide to carry dangerous goods ?
The dangerous goods declaration is needed to achieve the transportation of goods under the ADR scheme.
Mandatory in particular allows us to identify uploads qualitatively and quantitatively.
The main obligatory indications on the transport document are :
- ONU number with the letters “UN” before
- The official term for the transport
- Number of samples of label
- Packing group
- Number and description of packages
- Total quantity of each dangerous goods
- Name and address of the recipient
- Name and address of the sender
- Mention of any special agreement
- Tunnel classification code
For the regulated garbage, you can replace the transport document with waste disposal documentation. Some specific waste can have different documentation, such as asbestos.
The shipper has to give transportation advice to the vehicle team before the departure. It has to stay accessible to anyone in case of emergency or just to inquire. A training certificate from the driver and an identification document for each member of the team is needed in the vehicle.
How can you tell if a product is dangerous?
Each dangerous-to-transport item has been coded. In addition to his official designation (non-commercial name), he has been assigned an international identifying number:
The ONU number. This ONU number is made up of the following points, which represent the dangerous goods’ identity card:
- The level of danger, as well as any additional risks that may arise,
- The categorization code corresponds to a categorization of products based on their physical and chemical characteristics within each class of danger.
- Except for some products, the packaging group – GE – defines the level of danger that a product poses during transportation. The GE I classification corresponds to extremely dangerous goods, the GE II classification to moderately dangerous goods, and the GE III classification to low-risk goods,
- Special provisions: they are intended to supplement the ADR’s general application rules,
- The tunnel restriction code establishes the permissions for traffic to pass through tunnels.
How to choose appropriate packaging for dangerous goods?
A dangerous good must be carried in appropriate packaging. There are several things to respect such as the group of packaging and the different types of wrapping (barrel, bag…). Those instructions are given to the transport staff.
In order to identify goods that are in accordance with the ADR, specific markings are used. To know the compatibility between the goods and the wrapping but also the way to close the container, the step of the declaration of the packaging of the products is very important.
Example of labeling Example of indication of safe stacking load
Master the basic instructions of packaging allows you to avoid risks such as chemical reactions between content and containing.
There are several labels for dangerous substances:
Explosive substances and articles
Flammable gasses
Non-flammable gasses
Non-toxic gasses
Toxic gasses
Flammable liquids
Solid materials flammable solids, self self-reactive materials, materials polymerizing substances and explosive solids desensitized
Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gasses
Oxidizing substances
Organic peroxide
Toxic substances
Infectious substances
Radioactive substances
Fissile materials
Corrosive materials
Dangerous materials or articles
Some labels are supported by those:
Environmentally hazardous substance
Elevated temperature substances
Recognizing and identifying a dangerous good according to ADR
A good is identified as a dangerous good when it constitutes a danger for human beings or the environment. It must meet several criteria of classification. It can be a material, an object, a solution, a mixture, a preparation, or a waste.
Different forms of dangerous goods
According to ADR, the 9 forms of dangerous goods are:
- Explosive objects and materials
- Gasses
- Flammable liquids
- Flammable solids, self retroactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
- Substances liable to spontaneous combustion
- Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gasses
- Oxidizing substances
- Organic peroxides
- Toxic substances
- Infectious substances
- Radioactive substances
- Corrosive substances
- Dangerous substances and objects
DocShipper Tip
Docshipper Tip:The control of the packaging instructions and, more generally, of the rules of use of the packaging allows several risks, such as the chemical reaction between the container and the contents, the overflowing or bursting in case of non-respect of the filling rate of the packaging. For more information on the rules and risks to be avoided, we strongly advise you to contact one of our experts. They are there for you and will respond within 24 hours.
What documents must accompany the transport of dangerous goods?
The transport document
Any transport of goods, regulated by ADR, must be accompanied by a transport document commonly known as the “Declaration of Dangerous Goods”.
Mandatory information makes it possible to identify the load qualitatively and quantitatively.
The main mandatory information on the transport document is:
■ The UN number preceded by the letters “UN”,
■ The proper shipping name,
■ The packing group,
■ The model label numbers (the label number corresponding to the subsidiary risks is in parentheses),
■ The number and description of the packages,
■ The total quantity of each dangerous good,
■ The name and address of the consignor;
■ The name and address of the consignee,
■ A reference to any special agreement,
■ The tunnel restriction code.
For waste, specific documents can be used as a transport document for dangerous goods:
■ For asbestos waste: see CERFA form 11861-03 – BSDA,
■ For healthcare waste with infectious risks DASRI: see CERFA form 11351-04.
For mixtures classified in collective entries, or in “n.o.s.”, the proper shipping name shall be supplemented by the technical name of the substances constituting the mixture. Like what:
UN 1993, FLAMMABLE LIQUID N.O.S. (CONTAINING XYLENE AND BENZENE)
Written instructions for the vehicle crew
Instructions must be given by the carrier to the crew of the vehicle prior to departure, in one language(s) that each member can read and understand.
Be careful, the carrier must ensure that each member of the crew of the vehicle concerned correctly understands the instructions and is able to apply them.
These instructions must be placed inside the cabin and within easy reach.
Other on-board documents Other documents required on board include:
■ The driver training certificate,
■ An identification document with photograph for each crew member, in particular for safety reasons.
DocShipper Alert
Understanding labeling is necessary for loading a truck in accordance with the ADR regulations for cooperative loading of items, particularly foodstuffs, and explosives.
This also allows it to change its behavior in the event of an accident, such as spreading during loading or projection while filling, as well as describe the actions to be performed for the handling of risky items. If you still have questions, contact one of our experts. They are there to help you and accompany you in your steps.
What are the specificities for the loading/unloading/handling of hazardous materials?
The safety protocol to be established between the host company and the carrier for all loading and unloading operations and the rules laid down in ADR will be consistent. Knowledge of and compliance with these rules contribute to reducing the risk of accidents on site and throughout transport.
In particular, crew members are strictly prohibited from:
■ To open the packages,
■ To clean the vehicle if they notice a leak.
Other recommendations must be respected, for example:
■ Handle packages in accordance with the orientation arrows,
■ Arrange packages in such a way that the hazard labels are visible.
In addition to the requirements set out above, precautions should be taken for the handling of dangerous goods, in particular with regard to:
Prohibitions on joint loading
Only compatible goods are allowed in the same vehicle.
Compatibility should be checked according to the labelling of each package.
For example, particular care should be taken for goods labelled with labels 1, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6 which generally cannot be transported with other dangerous goods in the same vehicle.
Precautions relating to foodstuffs
ADR imposes special precautions on certain substances when they have to be loaded with foodstuffs. These are mainly toxic and infectious substances and certain Class 9 substances, which may be transported with foodstuffs only in compliance with certain rules laid down in ADR.
It is also appropriate to apply national rules laying down the technical and hygienic conditions applicable to the transport of food.
Handling and stowage
Packages containing dangerous goods shall be secured by appropriate means capable of restraining them.
Packages should not be stacked unless they are designed for. This is indicated on the packaging and in the marking of the package.
Particular attention must be paid to:
■ The means of securing (straps, etc.) so that they do not damage the packages,
■ Handling to prevent packages from being damaged by ground drag, shock and rough handling.
These recommendations are in addition to the rules of good practice that companies can put in place for the handling and stowage of loads, as well as the obligations mentioned in the standard contracts.
Examples:
For UN 3291 (hospital waste): packages should be stored in cool places, away from heat sources.
For UN 2984 (hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solution): it is forbidden to use highly flammable materials to secure packages.
No smoking
It is forbidden to smoke next to and in the vehicles during the handling of packages of hazardous materials.
Vehicle
It is prohibited to load/unload dangerous goods on public roads, except for a few exemptions
identified in the TDG Order.
In addition, it is prescribed to keep the vehicle engine stationary during the package handling phases (unless necessary for the operation of the mechanisms ensuring loading/unloading), and to immobilize the vehicle.
Choosing a dangerous goods transportation company
On the market, there are a diversity of road transport companies. However, none of them are equipped to convey hazardous goods via road.
Be aware that they are required to follow a number of regulations when loading, unloading, and implementing dangerous goods. These standards also differ depending on the social class to which they belong.
It is critical that you ask yourself five questions before deciding on your business. These five questions will lead you to the best logistical provider available, based on your needs.
Is it possible for the company to cover your area?
If you’re looking for a road transportation company, be sure to look into the following factors:
Is your delivery zone covered by the company? Is she following the rules of the sending and receiving countries? If you’re shipping
goods internationally, it’s critical to make sure your logistics partner follows the laws of the destination country.
If you need to use a multimodal mode of transportation, try to find one that can handle the complete delivery of your hazardous goods. In any case, ensure that your goods are in good working order, regardless of the form of transportation used.
Is it legal for a logistics service provider to deliver dangerous goods?
In our post on hazardous materials classes, we discovered that the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) had identified nine hazardous materials classes.
Because there are several sorts, you must ensure that the company with whom you wish to collaborate is authorized to carry the hazardous materials you require.
Is your company equipped with routable transportation vehicles?
ADR, as we saw in our last essay, is the text that governs all router transportation of dangerous goods.
It specifies the vehicle categories and kinds to be used based on the hazardous material being transported. During inspections mandated by the ADR of a float of engines, the company you choose must adhere to the following standards:
- Tractors and cargo vehicles are required to undergo an annual examination.
- Initial, annual, three-year, and six-year inspections are required of city trucks and city container drivers.
- Inspection prior to use, after one year, at the end of two years and a half, and once the five years of use have been completed.
Is his team well-versed in the transport of hazardous goods?
Keep in mind that it is critical that the individuals in charge of the loading, and unloading of dangerous goods be trained. Indeed, as you are aware, for reasons of safety, we do not charge or discharge dangerous goods, nor do we charge or discharge any other type of goods. There are also numerous training programs aimed at preparing operators and transporters for the safety standards that apply to the transportation and storage of these products.
In addition, your logistics provider should have a security advisor on staff. His primary responsibility is to ensure that no risks are created and that safety standards are followed.
What is the price per mile that she offers?
In most cases, the logistical companies’ offer of transportation for dangerous goods is transport by lots completes (or charge complete), which is done door to door.
This type of transportation offer entails taking custody of your goods as soon as they leave your store, resulting in a higher price.
It’s worth noting that it’s always a good idea to ask your logistics provider for a list of all of his prices. As a result, you’ll be able to assess all the options available to you and choose the one that best suits your needs.
DocShipper Tip
DocShipper Advice: If after reading this article, you have additional questions, do not hesitate to contact our experts, they are here to answer all your questions and help you. To do so, simply fill out this contact form. And if you want to know more about the services we offer at DocShipper, you can visit our official website
FAQ | Transportation of Dangerous Goods
Read more
Looking for more? These articles might interest you:
DocShipper info: Do you like our article today? For your business interest, you may like the following useful articles :
- Coronavirus (Covid-19) impacts on import/export business
- How does Coronavirus impact international supply chain?
- 💡How to find a good product to sell?
- How to find your reliable supplier for your business? [Fair Trade Guide]
- AliExpress | Use the Chinese panacea to sell your products online
- How a sourcing strategy can rocket your margin?
Need Help with Logistics
or Sourcing ?
First, we secure the right products from the right suppliers at the right price by managing the sourcing process from start to finish. Then, we simplify your shipping experience - from pickup to final delivery - ensuring any product, anywhere, is delivered at highly competitive prices.


Fill the Form
Prefer email? Send us your inquiry, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Contact us