Rail Freight from/to the U.K.
Optimise your transit times and logistics budget with rail freight connecting China and Asia directly to the U.K. and Europe, including regular corridors from China to the U.K. by train.
Rail Transport Between is in Average..
70 % cheaper than air freight
Rail freight can reduce costs by up to 70% compared to air transport, making it a cost-effective option for non-urgent but valuable goods. For many U.K. companies, this is the perfect balance between speed and budget.

50 % faster than sea freight
Transit times average 15 to 20 days between China and Europe, which is up to 50% faster than ocean freight. With established rail services reaching directly into the U.K., importers and exporters now benefit from delivery times that are significantly shorter than traditional sea routes.


Rail Freight: A Strategic Alternative for Your Cargo
While sea and air remain the most widely used transport modes, rail freight has become an increasingly attractive option for trade between Asia and Europe. With dedicated corridors crossing China, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe before reaching the U.K., businesses gain a powerful solution that shortens delivery times while keeping costs under control.
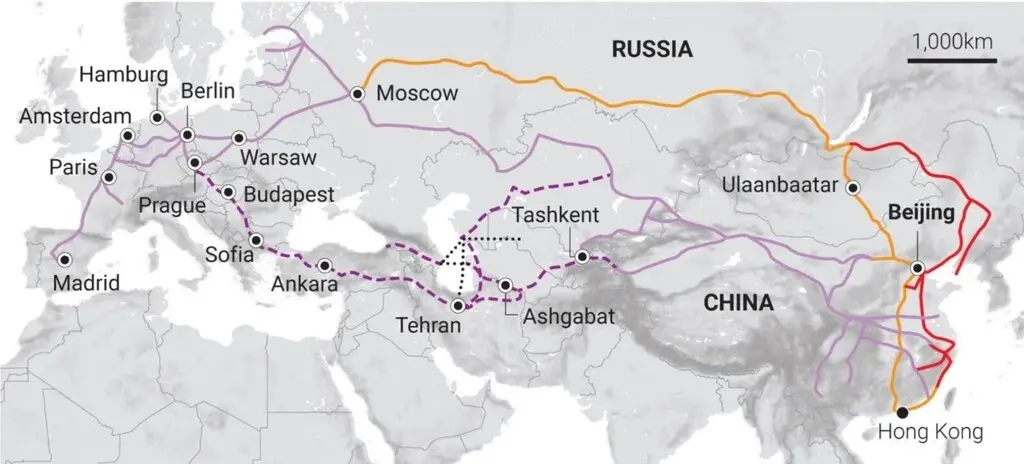
Our Rail Freight solutions

Full Container Load (FCL) for Large Shipments
Shipping a full container by rail is ideal for large, regular shipments that demand a secure and uninterrupted journey. Containers move directly from the origin station in China to the U.K. or European hub without being opened or handled, ensuring maximum security and efficiency while reducing cost per unit shipped.
Less than Container Load (LCL) for Shared Cargo
When volumes are smaller, LCL by rail provides a flexible and affordable option. Your cargo is consolidated with shipments from other companies, allowing you to access the benefits of rail without paying for a full container. This solution makes rail freight accessible to smaller businesses while connecting directly to Europe’s distribution networks.
From the Rail Station to Your Door
Rail freight rarely operates alone. That’s why DocShipper U.K. integrates rail into complete intermodal solutions. We combine rail with trucking or maritime legs to ensure that your cargo is collected from the supplier and delivered right to your warehouse or retail outlet. With fewer handling points and optimised routes, your supply chain benefits from lower costs, improved security, and faster end-to-end delivery.
Adapting in Real Time to Avoid Blockages
Rail corridors can face disruptions such as congestion, weather, or geopolitical issues. At DocShipper, we don’t let your supply chain stop. If a terminal in Europe is blocked, we reroute through alternative hubs and arrange onward delivery by road or sea. This flexibility ensures that your goods continue moving and your business remains protected against unexpected events.
Need a Custom Route for Your Rail Shipments?
Let’s explore all the options to keep your deliveries secure, efficient, and on track.


Why Choose DocShipper U.K.
Cargo Consolidation
We reduce costs by grouping your cargo with others for shared efficiency.
Door-to-Door Solutions
Solutions From your supplier in China to your warehouse in the U.K. or Europe, we manage the entire journey under one contract.
24/7 Support
A dedicated logistics expert is available at any time to answer questions and provide updates.
Local Presence and Global Network
With teams based in China, the U.K., and across Europe, we manage and track your shipment seamlessly from origin to destination.
6100 +
Clients9200 +
Operations230 +
CBM shipped4.8 +
client reviewsClients Testimonials
We can't make this up - See why businesses worldwide trust us with their shipments every day.
I contacted DocShipper to organize the import of board games from Asia to Switzerland. Despite my lack of experience in the field and the modest size of my request, my dealings with the staff were always professional and efficient. I received sound advice and the staff always took the time to answer my questions. I look forward to working with DocShipper for the import of my goods and highly recommend their services.
Mavrik Grangier
December 10, 2024My name is Ad Van Den Bosh. I am a Dutch business man cross-trading in the Far East. I reached Robert Houwayek (DocShipper's representative) to clear a 40HC of greenhouse equipment from Qingdao, and deliver it to Lan Krabue in no time. He suggested that I request a Form E, which I did from the supplier, and was able to enjoy a preferential tariff treatment. DocShipper, a way to help you save both time and money!!
Ad van den Bosch
March 5, 2024I recently used Docshipper to ship my appliances from Germany to Thailand, and I'm thrilled with the service I received! [...]The team was professional, responsive, and kept me informed every step of the way. The packaging and handling of my appliances were top-notch, and they arrived in perfect condition. I was impressed with the attention to detail and care taken to ensure a safe and successful transport. I really recommend Docshipper for it.
Chemmie Chatuphorn
November 28, 2024In the event of goods being stuck at customs, Robert [...] is a customs broker you should arguably consider to release your cargo. Once I knew that my scale modeling tools coming from Spain are being withheld at Suvarnabhumi Airport, I resorted to him to release it and handle the last mile delivery. All what he asked me is to send 2 emails to be able to do it! [...] Well guess what, within 48 hours, it was done! I got my parcel at my place in Phuket.
Chan chan
Mar 5, 2024A vice president caught up in the thick of thin things, an EXW shipment of plumbing supplies for irrigation from Eureka California to Costa Rica is definitely not what I’d like to have on my agenda. Robert’s hang-in-there posture toward any arising challenges in shipping. [...] skillfully handled all US export formalities incl. SED/AES filing, not to mention the sea freight from Oakland POL. Everything ended up working out like a charm!
Dave Sheppard
July 10, 2024I feel they covered everything. DocShipper shipped a 20- ft Milvan overseas to Laem Chabang for a customer. The team was responsible for shipping the shipping to another country. Having very little knowledge in this area, I didn't know how to organise myself . One week after my arrival on the Asian continent. Marc O. Was available at all times and nearly instant feedback. Made a stressful event much easier and he definitely knows his job.
Anonymous, Indiana
Aug 9, 2023Not Sure if Rail Freight is Right for You?
We analyse your needs and advise on the best option, rail, sea, or air, to help you save costs and minimise risks.