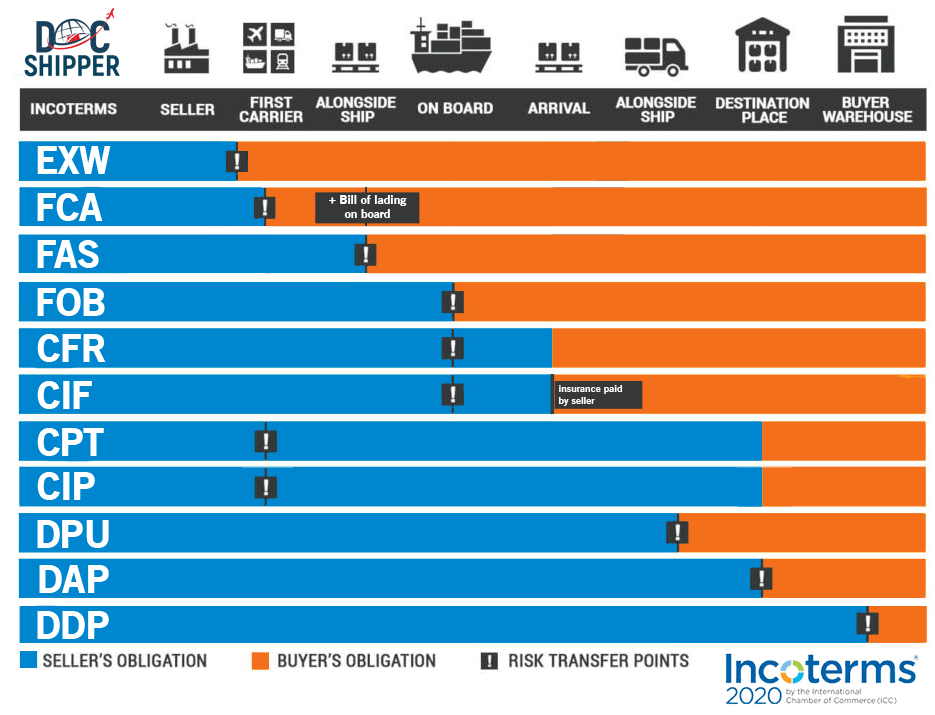
Although they are an integral part of our daily life, most people do not know much about Incoterms or freight in general since it is quite a difficult subject to deal with. Docshipper therefore offers you this guide to provide you with complete information on the Incoterms , clearly explaining each of them in a way that everyone can understand. Good reading !
Use of Incoterms
Freight Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are the standard contractual term used in import/export sales contracts to define responsibility and obligation for the shipment of goods . In short, this makes it possible to know from where the supplier must ensure that the goods are transported as well as when the buyer must take care of the shipping process.
In total, there are 11 incoterms, but the best known are FOB ( Free On Board ), EXW ( Ex Works ) and FCA ( Free Carrier ).
DocShipper Alert
Incoterms can be confusing or easily misunderstood because they are legal terms, and choosing the wrong one can turn your shipment into an expensive nightmare. This is why it is important to find out about them and to agree on the most advantageous incoterm for you.
When should we consider using Incoterms ?
The best time to use incoterms is before the negotiation of the sales contract since it avoids unnecessary complications during shipping.
Main country-specific differences
Customs procedures are much more flexible at borders that can be crossed quite easily, such as within the EU. The other three exceptions that may affect shipments are: the United States is the only country that requires a customs bond, importing to the United Kingdom requires a Deferment Account, and exporting from India includes a withholding tax.
DocShipper Alert
Some freight forwarders prefer to use only a preferred set of Incoterms because they “seem to work“. So don’t be surprised if some freight forwarders delay your choice of incoterms, even if it is the most appropriate incoterm for your shipment. At Docshipper we will never do that, because we always put our customer’s interest first. Contact us now for your shipping needs.
What Incoterms do not cover
Incoterms do not cover property rights , possible cases of force majeure and breach of contract. They must be included in the sales contract. Similarly, all incoterms, except for terms beginning with “C”, do not assign liability to the insurance organization. Cargo insurance is therefore a separate cost for buyers.
DocShipper Tip
Do not hesitate to consult our page concerning transport insurance if you wish to know more about this subject.
How to define the designated place in the sales contract ?
In the sales contract, the place of shipment must be indicated immediately after the chosen incoterm, for example ” FCA Shenzen Yantian CFS “.
In the sales contract, the place of shipment must be indicated immediately after the chosen incoterm, for example ” FCA Shenzen Yantian CFS “.
DocShipper Tip
Be specific when setting the location, especially in large cities which may have multiple terminals, and in large terminals which may have multiple drop-off points.
The impact of incoterms on your shipping costs
For example, when shipping EXW, you will have to bear the additional cost of getting your goods from your supplier to the seaport or airport. It is therefore necessary to pay attention to which incoterm you choose in relation to the containers, boxes or pallets, your dimensions and your weights in order to choose the incoterm which will be the most useful to you and which will also cost you the least.
How do letters of credit limit the choice of incoterm?
If the sale is by letter of credit or documentary credit , the channel releasing the funds must first provide the bank with several documents, including a bill of lading or air waybill . When trust between buyer and seller is restricted, a letter of credit is used. This does not include the EXW letter of credit, as the supplier will be paid before removal. Interpretation of international trade terms.
The “F” incoterm requires trust, because if the buyer cancels an international shipment, the supplier will not submit the bill of lading to the bank. Incoterms beginning with “D” generally require trust, as the seller bears all shipping costs. Therefore, the four “C” incoterms are still the best choice for letters of credit .
DocShipper Tip
DocShipper Advice : We advise you to inquire about sea freight as well as air freight to find out which is best for your needs. Contact us now for your shipping needs.
The different incoterms
What is EXW (Ex Works)?
For EXW (Ex Works) shipments, the buyer arranges the complete shipment, from the supplier’s warehouse to the final destination of the shipment.
Who is responsible for what?
Buyer is responsible for almost every step during shipping. The seller, on the other hand, is only responsible for the bill of lading or air waybill and must ensure that the goods are available for collection at the place indicated, generally at the factory, on a date agreed with the forwarding agent.
Is it a good choice ?
This is probably not a practical arrangement, as the buyer is generally in a much worse position than the seller to arrange the tasks in the country of export. These tasks include loading the truck, arranging specialist equipment for loading if required, documentation (the seller is only obligated to assist in obtaining an export license, certificate of origin, etc. – and is not even required to provide packing lists or fumigation certificates); and export clearance management.
EXW Tips and Tricks
- If the seller needs to help load, be sure to include that point elsewhere in the sales contract.
- This shouldn’t be a problem if you’re importing from China, but when choosing a freight forwarder, check that they can arrange export clearance.
- The buyer is not obliged to draw up a transport contract. This means that the buyer can sell the goods to a customer, who will then collect them.
- Exporters must submit a courier receipt or FCR to the buyer’s freight forwarder, rather than submitting the air waybill or bill of lading.
- Exporters will not have direct proof of export, though they can otherwise claim a refund of domestic sales tax.
What is FCA (Free Carrier)?
For FCA (Free Carrier) shipping , the seller takes care of most of the steps in the country of export (such as dealing with customs as well as trucking in the country of export) . The buyer, on the other hand, takes care of arranging all the other steps until the final destination of the cargo.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller must take care of all that is necessary to do in his country until the goods are delivered to the carrier at the place indicated. However, the buyer may be responsible for certain tasks in the country of export if the named place is not the final terminal.
DocShipper Tip
This is a recommended Incoterm for containerized freight. FCA overcomes the drawbacks of EXW, where the buyer is in a less favorable position than the seller to arrange transport and local customs. Contact us now for your shipping needs.
Tips and Tricks
- The seller remains responsible for loading the truck at its premises and the carrier is responsible for unloading the truck at the final location if the named final location is a freight forwarder’s warehouse or other terminal that is not the port . maritime or airport,
- The buyer is responsible and liable for transportation and terminal charges in the country of export.
- The named place can also be the supplier’s factory , which makes it similar to EXW, except the supplier is responsible for loading the truck.
DocShipper Tip
Regardless of the designated location, the seller is always responsible for all export and documentation tasks. There is an exception, which only concerns payments by letter of credit : the buyer can now ask the carrier to add the word “on board” to the bill of lading. Contact us now for your shipping needs.
What is FAS (Free Alongside Ship)?
The FAS (Free Alongside Ship) is a shipping incoterm. For FAS shipment, the seller arranges all steps from the country of export and the buyer has to take care of all other steps until the final destination of the cargo.
Who is reSponsible for what?
The seller is responsible for all steps in his country until the goods are in the ship for sea freight or in the terminal warehouse in the case of air freight. The buyer, on the other hand, is responsible for loading the goods
DocShipper Tip
This is an Incoterm not recommended for containerized freight, FAS is designed for bulk and break bulk freight instead.
Is it a good choice ?
There is no obvious reason why the buyer would want to be responsible for only one task in the country of export – loading containerized freight. Consider the FOB formula instead, which is exactly the same as the FAS formula, but has the added benefit that the seller is responsible for loading the vessel.
What is FOB (Free On Board)?
FOB (Free On Board) is a shipping incoterm. For FOB shipment, the seller has to take care of all the steps in the country of export. The buyer, on the other hand, must organize all the other steps until the final destination of the goods.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller is responsible for all steps in his country until the goods are loaded on the plane or aircraft.
DocShipper Tip
This is an incoterm not recommended for LCL air or sea freight, however we invite you to read the following points.
Tips and Tricks
The FOB incoterm is not suitable for LCL or airfreight as there is an intermediate stage for the consolidation of the load which is that the named place of delivery is the consolidation facility, not the vessel or the aircraft . Therefore, the buyer will be responsible for the rest of the freight charges and terminal charges. If you want to do LCL as well as air freight, DocShipper recommends that you consider FCA instead.
DocShipper Tip
DocShipper Advice : Be sure to check out our Complete Guide to FCL Containers and LCL Containers to learn more about these two different categories.
What is CPT (Carriage Paid To)?
The CPT (Carriage Paid To) is a delicate incoterm being mainly recommended if you use a letter of credit.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller is responsible for all procedures in his country, or to the warehouse of the buyer’s forwarder. The seller is also responsible for booking the main transport to a terminal in the buyer’s country, or even further to the buyer’s warehouse. Anyway, the seller is not responsible after the goods arrive at the terminal or warehouse in his own country.
Is it a good choice ?
Importers who do not have a representative at the port should be wary of using this term unless they are sure that the carrier’s tariffs include terminal handling charges. The consequences would be that your seller’s freight forwarder will use a third-party agent to handle import clearance, duties and terminal fees. Many importers get caught with way too high fees and dubious duties that they actually can’t dispute.
Tips and Tricks
On the other hand, this incoterm is often an excellent choice for large importers , if they have an agent responsible for the goods once they have reached the terminal in the country of import.
The seller is not responsible for the intermediary (except if it is indicated in the sales contract) if there is more than one transport in the country of export.
Risk and liability ( for duties and payment ) are transferred to different points for Conditions C. Risk is transferred to the country of export when the carrier receives the shipment (at the named place of delivery) , even if the buyer has booked and paid for the main transport.
The buyer must also take out insurance from the place where the responsibility is transferred (named place of delivery) , ie the terminal of the country of export.
One of the four C terms must be chosen when the sales contract includes a letter of credit.
What is CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid to)?
Who is responsible for what?
CIP (Carriage And Insurance Paid To) means that the seller is responsible for the delivery, delivery costs and insurance costs of the goods until they are transferred to the first carrier responsible for the transport of the goods. Once this delivery has been made, the buyer assumes full responsibility.
If you plan to ship your goods through CIP, be sure to read the details of your contract carefully.
What is the difference between CIP and CIF ?
These two international trade terms are very similar, the difference is that CIP applies to all modes of transport , while CIF only applies to ocean freight . This also means that for CIF the responsibility is transferred to the origin seaport, and for CIP the responsibility is transferred to any agreed location in the country of origin. The CIP incoterm is also very similar to the CPT incoterm, except that for CIP, the seller is also responsible for setting up substantial transport insurance.
What is the difference between CIP and CIF ?
These two international trade terms are very similar, the difference is that CIP applies to all modes of transport , while CIF only applies to ocean freight . This also means that for CIF the responsibility is transferred to the origin seaport, and for CIP the responsibility is transferred to any agreed location in the country of origin. The CIP incoterm is also very similar to the CPT incoterm, except that for CIP, the seller is also responsible for setting up substantial transport insurance.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
What is CFR (Cost and Freight)?
The CFR (Cost and Freight) is a delicate shipping incoterm. Read the details carefully. Not recommended.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller is responsible for all steps in his country up to the loading of the goods on board the ship and is also responsible for the main transport.
DocShipper Tip
This is an Incoterm not recommended for containerized freight, CFR is designed for bulk and break bulk freight instead.
Is it a good choice ?
As for FOB, this incoterm is suitable for FCL, but not for LCL and airfreight ( see FOB ).
Additionally, importers who do not have a representative at the port should be wary of using this term unless they are sure that the carrier’s rates include terminal handling charges. Otherwise, your seller’s freight forwarder will use a third-party agent to handle import clearance, duties and terminal dues. Many importers get caught with inflated fees and dubious duties that they effectively cannot dispute.
Tips and Tricks
Refer to the CPT.
What is CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight)?
The CIF (Cost, Insurance, And Freight) is a delicate shipping incoterm. Read the following details carefully.
Who is responsible for what?
This incoterm works exactly like the CPT, except that the seller is also responsible for insuring the main transport.
DocShipper Tip
This is anIincoterm not recommended for containerized freight, CIF is designed for bulk and break bulk freight instead.
Is it a good choice ?
Refer to the CPT
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
What is the DPU incoterm (Delivered at Place Unloaded)?
DocShipper Tip
Prior to the publication of the ICC Incoterms 2020 update, this Incoterm was known as DAT, however this name change does not infect its content.
The DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded) is a maritime incoterm. For DPU shipment, seller bears all charges related to export country and international transit. The buyer takes care of the rest.
This incoterm can cause problems because it involves two freight forwarders at a critical point.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller retains the responsibility and risks in the country of importation, until the cargo is unloaded. This can happen in several places, including at the port, inland terminal or freight forwarder’s warehouse.
Is it a good choice ?
This rule favors the seller when he is stronger, being responsible for all tasks in the country of export; and favors the buyer when the latter is stronger, being responsible for all tasks in the country of importation. The seller is also responsible for the main freight. Also consider the DAP with a terminal as the designated place, where the buyer pays for unloading.
Is it a good choice ?
This rule favors the seller when he is stronger, being responsible for all tasks in the country of export; and favors the buyer when the latter is stronger, being responsible for all tasks in the country of importation. The seller is also responsible for the main freight. Also consider the DAP with a terminal as the designated place, where the buyer pays for unloading.
Tips and Tricks
The seller pays for the unloading. The buyer is responsible for all charges after unloading, except (in theory) charges caused by delay, including terminal demurrage charges, which are generally the responsibility of the seller.
This exception may give rise to disputes. The seller has good reason to refuse to pay if the buyer has delayed import customs clearance. But, maybe it’s because the seller made a mistake in his presentation. Maybe it was the customs broker’s mistake. Consider ways to avoid this type of dispute when negotiating the contract , such as telling the seller to mail certain documents to the buyer before pick-up; liability for demurrage and other costs takes into account the above scenario, all information on documents to be submitted to customs should be double checked. Basically, the buyer,. Or, consider CPT (delivery to buyer’s warehouse) instead.
Make sure that the seller can complete all the necessary formalities in the buyer’s country, such as paying GST or VAT .
The damage is more likely to occur between the buyer’s premises and the importing country’s terminal than the last leg to the buyer’s warehouse. However, this can be difficult to prove. Consider DAP instead.
If the named place is a Customs Clearance Depot , or for more porous borders where Customs pre-clears at the border, the shipment may be delivered to the named place without customs clearance. In other words, payment at customs is always required.
Tips and Tricks
The seller pays for the unloading. The buyer is responsible for all charges after unloading, except (in theory) charges caused by delay, including terminal demurrage charges, which are generally the responsibility of the seller.
This exception may give rise to disputes. The seller has good reason to refuse to pay if the buyer has delayed import customs clearance. But, maybe it’s because the seller made a mistake in his presentation. Maybe it was the customs broker’s mistake. Consider ways to avoid this type of dispute when negotiating the contract , such as telling the seller to mail certain documents to the buyer before pick-up; liability for demurrage and other costs takes into account the above scenario, all information on documents to be submitted to customs should be double checked. Basically, the buyer,. Or, consider CPT (delivery to buyer’s warehouse) instead.
Make sure that the seller can complete all the necessary formalities in the buyer’s country, such as paying GST or VAT .
The damage is more likely to occur between the buyer’s premises and the importing country’s terminal than the last leg to the buyer’s warehouse. However, this can be difficult to prove. Consider DAP instead.
If the named place is a Customs Clearance Depot , or for more porous borders where Customs pre-clears at the border, the shipment may be delivered to the named place without customs clearance. In other words, payment at customs is always required.
What is DAP (Delivered At Place)?
DAP (Delivered At Place) is a maritime incoterm. For DAP shipping, seller arranges all shipping except import customs.
Who is responsible for what?
The seller continues to bear the responsibility and risk in the country of import, usually at the buyer’s preferred warehouse (own, FBA’s, freight forwarder’s, etc. ). However, as with FCA, the designated place can also be the terminal.
Is it a good choice ?
This is probably not a practical arrangement, as the seller is generally in a much worse position than the buyer to arrange the tasks in the country of import.
Is it a good choice ?
This is probably not a practical arrangement, as the seller is generally in a much worse position than the buyer to arrange the tasks in the country of import.
Tips and Tricks
All of the tips and tricks for the DAT also apply to the DAP, except for the first one – responsible for offloading. For the DAT, the seller is responsible for unloading. For DAP, the buyer is responsible for unloading.
If the terminal is chosen as the named place, the DAP is exactly the same as the DAT, except that the seller pays for the offloading.
Tips and Tricks
All of the tips and tricks for the DAT also apply to the DAP, except for the first one – responsible for offloading. For the DAT, the seller is responsible for unloading. For DAP, the buyer is responsible for unloading.
If the terminal is chosen as the named place, the DAP is exactly the same as the DAT, except that the seller pays for the offloading.
What is DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)?
For DDP (Delivery Duty Paid) shipments , the seller arranges all shipping , including import customs.
Who is responsible for what?
Seller is responsible for all shipping. The buyer is only responsible for unloading the goods, including customs clearances and import payments. The designated place of delivery is generally the warehouse chosen by the buyer.
Is it a good choice ?
The seller is generally in a much worse position than the buyer to organize the tasks in the country of import, so this may not be the best arrangement as the consequences can attract several problems (see tips and tricks) . Less experienced importers should probably avoid this incoterm and consider DAP instead .
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
Tips and Tricks
Care must be taken since in some countries such as the United States, freight forwarders are not authorized to carry out customs clearance. The supplier must therefore be registered as an importer , otherwise he will not be able to carry out customs clearance. Suppliers must also have experience as importers. Clearance of imports is complicated and if the process is not followed exactly, the shipment risks being detained by customs. Therefore , the seller should insist that a copy of the entry documents be provided by the customs clearance agent soon after they are presented, in order to verify that there are no errors. In some countries, customs accept corrections in a timely manner.
Domestic product sales tax can only be paid by locally registered businesses. If the seller is not registered, the buyer will likely be liable for sales tax. There is a workaround by qualifying the rule, for example “Delivered Duty Paid”.
The DDP does not specifically require the seller to undertake import clearance. Buyer and Seller may agree that Buyer undertakes this task instead.
If the buyer offers to clear the goods for the seller, he must insist on using his own customs clearance agent . Otherwise, he risks losing control of the location of the cargo. They could end up liable for unnecessary costs, including demurrage and storage. This problem can be remedied by specifying elsewhere in the sales contract that the buyer is not responsible for any additional costs caused by a clearing agent’s error and that he is not responsible for any costs beyond a short period (2-3 days) after release from the carrier.
FAQ | All about incoterms [COMPLETE GUIDE]
Read more
Looking for more? These articles might interest you:
DocShipper info: Do you like our article today? For your business interest, you may like the following useful articles :
Need Help with Logistics
or Sourcing ?
First, we secure the right products from the right suppliers at the right price by managing the sourcing process from start to finish. Then, we simplify your shipping experience - from pickup to final delivery - ensuring any product, anywhere, is delivered at highly competitive prices.


Fill the Form
Prefer email? Send us your inquiry, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Contact us